
When you plan a trip through Tanzania's wilds, you often put excitement ahead of health preparation. But your health in Tanzania is just as important as your passport, especially if you're going to explore rural areas, look for the "Big Five," and climb Mount Kilimanjaro.
Tanzania has famous safaris and a lot of different ecosystems, but the country also comes up with its specific travel health requirements and environmental challenges. Hence, being medically ready for your trip will make it go more smoothly and give you more memories.
This guide covers everything from Tanzania travel insurance, food safety, packing lists, and emergency medical care. It also talks about vaccines and entry requirements. With all this handy information, we’re sure you’ll feel safe while travelling to different Tanzania Safari Destinations.
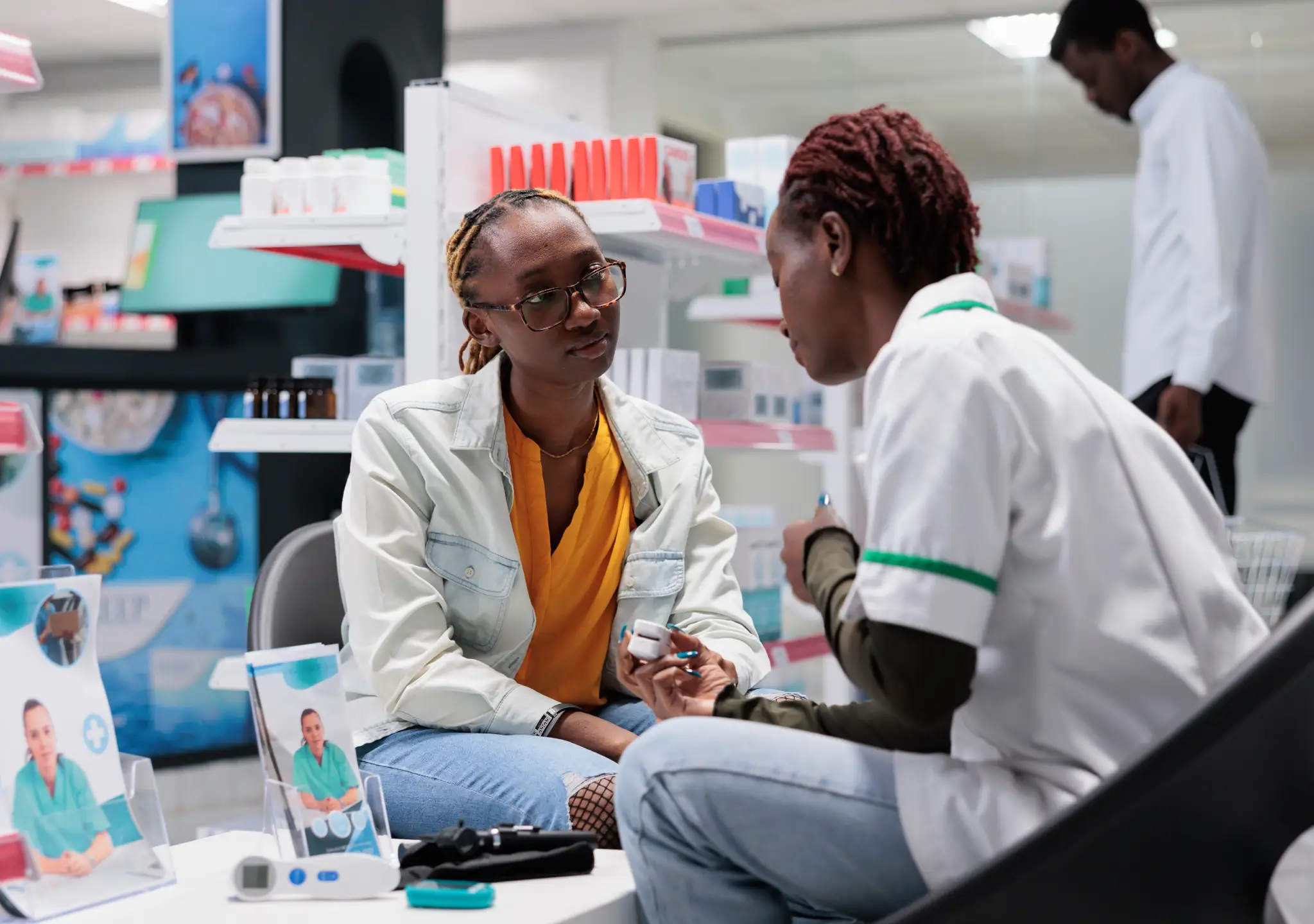
Before your Tanzania Safari Tour, make sure you follow the country's health-related entry rules. These can be different based on where you are transiting from or your region of origin.
For all the latest information on health and travel safety, please refer to the website of the Tanzania Ministry of Health.
You can also visit the official Tanzania Immigration Services portal to check visa eligibility and application requirements.
It is strongly suggested that you see a travel health clinic 6 to 8 weeks before your trip. Getting vaccinated against common illnesses in the area helps keep problems at bay.
Apart from the yellow fever, below are some of the vaccinations required when travelling to Tanzania.
For the detailed vaccinations and medications list, please visit the official CDC website.

Tanzania’s health infrastructure is strongest in major cities like Arusha, Dar es Salaam, and Moshi. Rural clinics may offer limited care, so pack a personalised travel health kit:
Consult a travel clinic for personalised advice and regional alerts. Use resources like the Healthy Travel Packing List for a detailed list of medicines you would need on a Tanzania Safari Tour.
Malaria is a major risk practically everywhere in Tanzania. The cases of Dengue are also increasing, particularly along the coast. Hence, one of the most important Tanzania Travel Health Tips is to take all the possible measures to avoid being bitten by mosquitoes. A few of them are:
Lastly, get medical help right away if you get a fever, joint pain, or a rash. Take pain relievers like ibuprofen less often until you are sure you don't have dengue. They can make you more likely to bleed. Take paracetamol if you have a fever.

Apart from mosquito bites, there are other health risks involved when travelling to Tanzania Destinations for safaris. Some of the risks and your approach to handling them effortlessly are described below:
Rabies is a problem in Tanzania, especially in rural places and near national parks. It can be spread by monkeys, stray dogs, and bats. In case you get bitten or scratched, do the following:
Are you planning a multiday walk, doing charity work or visiting faraway villages on your Safari Tours in Tanzania? You might want to get a rabies shot before being exposed.
Tanzanian cuisine is flavorful, but standard hygiene practices are not guaranteed. Poor food handling can lead to stomach upsets or serious infections. Some food safety tips you can follow are:
Tanzania's weather varies widely. There are hot and humid coastlines, and there are also chilly Crater Highlands. Altitude can affect even fit travellers, and dust is common on safari drives. Below are some things you can do to cope with heat and altitude:
For more gear suggestions based on terrain, check our Tanzania Safari Packing List.

It is a long established fact that a reader will be distracted by the readable content of a page when
We use equipment of international standards & our guides are trained in First aid & personal protection equipment
We use equipment of international standards & our guides are trained in First aid & personal protection equipment
We use equipment of international standards & our guides are trained in First aid & personal protection equipment
Our travel guide is made to save you time. It points you to the right parks, climbs, and activities, while sharing tips only locals know. Your dream Tanzania trip starts with good information, and we’ve put it all together for you.
We believe travel should never feel like a template. That’s why we design each safari or climb with you in mind. Whether you dream of quiet mornings by the crater rim or standing on Africa’s highest peak, we make it happen. Every route, lodge, and experience is chosen to fit your idea of perfect travel.